












- 12 sights
- 0 h 21 min
- 1.81 km / 1.12 mi
Sights

Montmartre Carousel

Basilica du Sacre-Coeur de Montmartre
The Basilica of the Sacred Heart of Paris, commonly known as Sacré-Cœur Basilica and often simply Sacré-Cœur (French: Basilique du Sacré-Cœur, pronounced [sakʁe kœʁ]), is a Roman Catholic church and minor basilica, dedicated to the Sacred Heart of Jesus, in Paris, France. A popular landmark, the basilica is located at the summit of the butte Montmartre, the highest point in the city. Sacré-Cœur is a double monument, political and cultural, both a national penance for the defeat of France in the 1870 Franco-Prussian War and the socialist Paris Commune of 1871 crowning its most rebellious neighborhood, and an embodiment of conservative moral order, publicly dedicated to the Sacred Heart of Jesus, which was an increasingly popular vision of a loving and sympathetic Christ. The Sacré-Cœur Basilica was designed by Paul Abadie. Construction began in 1875 and was finished in 1914. It was consecrated after the end of World War I in 1919.
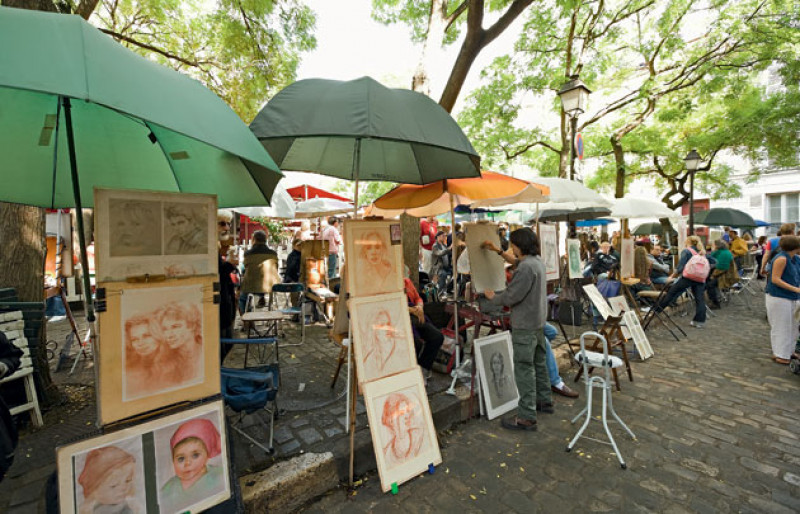

Place du Tertre
The Place du Tertre is a square in the 18th arrondissement of Paris. Only a few streets away from Montmartre's Basilica of the Sacré Cœur and the Lapin Agile, it is near the summit of the city's elevated Montmartre quarter. With its many artists setting up their easels each day for the tourists, the Place du Tertre is a reminder of the time when Montmartre was the mecca of modern art. At the beginning of the 20th century, many painters including Pablo Picasso and Maurice Utrillo were living there, some at the nearby Le Bateau-Lavoir. The Musée de Montmartre, the former home and studio of Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Suzanne Valadon, and the L'Espace Salvador Dalí, a museum principally dedicated to the sculpture and drawings of Salvador Dalí, can be found near Place du Tertre.
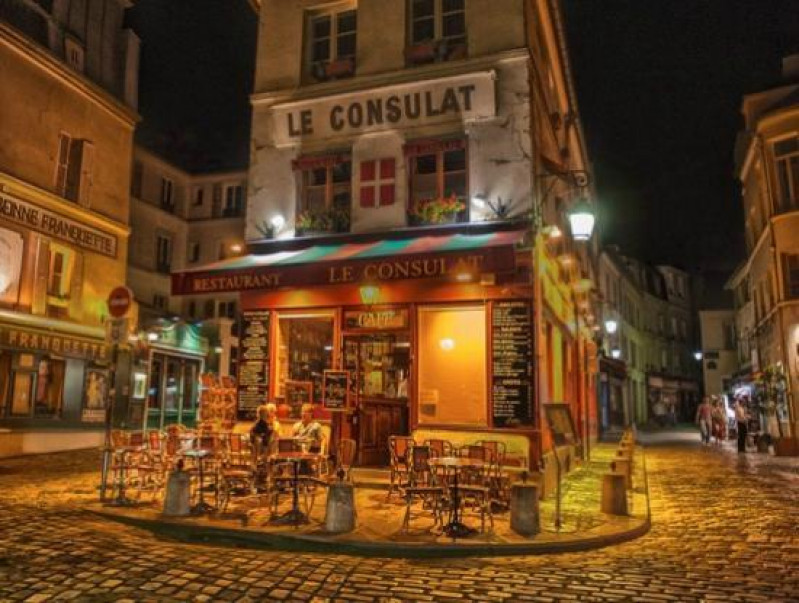

Le Consulat
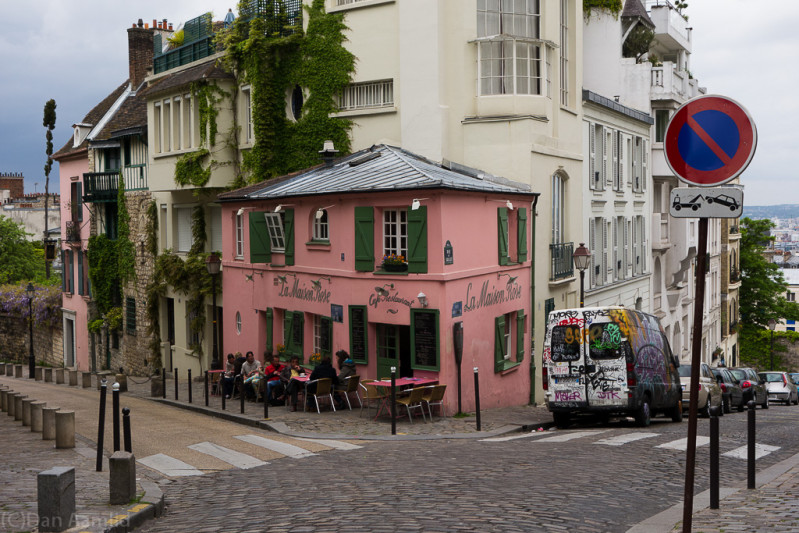
La Maison Rose
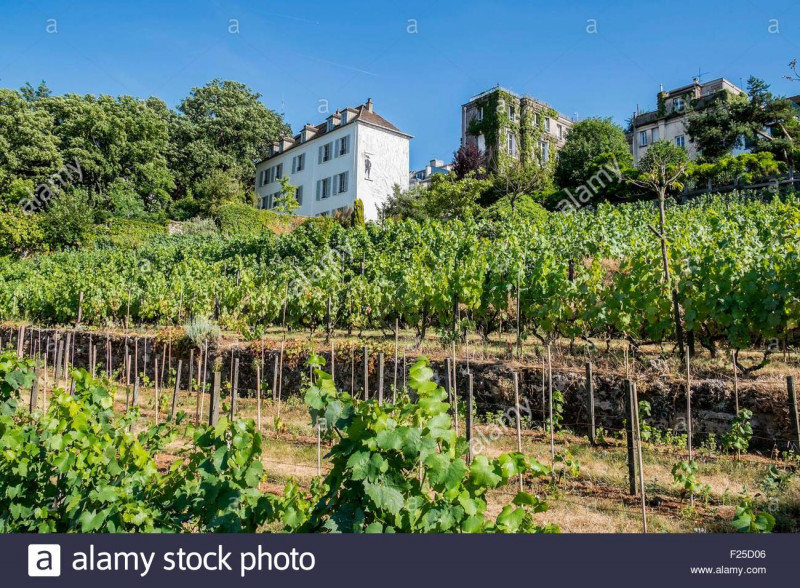

Clos Montmartre

Rue de L'Abreuvoir

Place Dalida
The Place Dalida (French pronunciation: [plas dalıda]) is the square of Montmartre, Paris, dedicated to the diva of French music, Dalida. Many fans and tourists visit to pay tribute to the French, Italian and Egyptian icon.

La Passe-Muraille
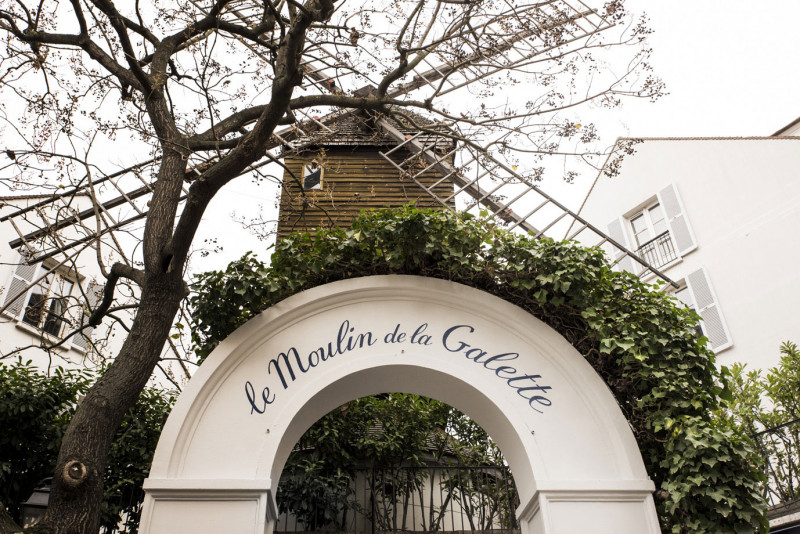

Moulin de la Galette
The Moulin de la Galette is a windmill and associated businesses situated near the top of the district of Montmartre in Paris. Since the 17th century the windmill has been known for more than just its milling capabilities. Nineteenth-century owners and millers, the Debray family, made a brown bread, galette, which became popular and thus the name of the windmill and its businesses, which have included a famous guinguette and restaurant. In the 19th century, Le Moulin de la Galette represented diversion for Parisians seeking entertainment, a glass of wine and bread made from flour ground by the windmill. Artists, such as Renoir, van Gogh, and Pissarro have immortalized Le Moulin de la Galette; likely the most notable was Renoir's festive painting, Bal du moulin de la Galette.
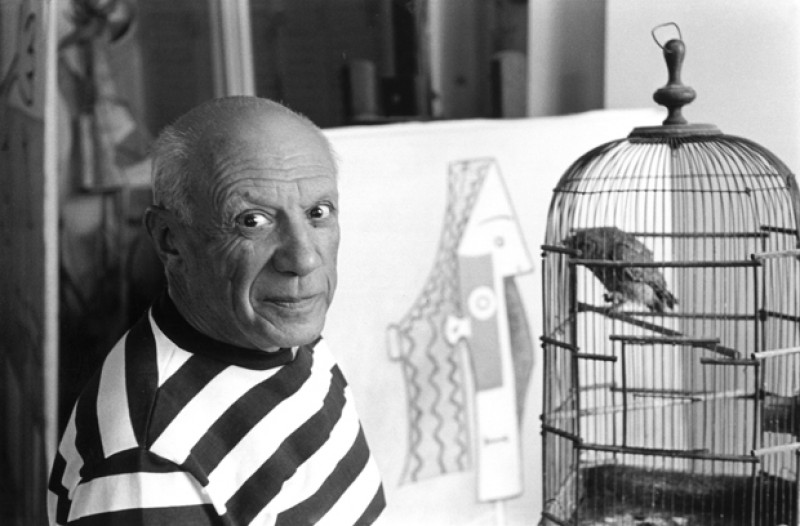

Picasso’s Paris Studio

Le Mur des Je T’aime
Share on Pinterest
